While both involve foreign currency, forex trading and money exchange offer two very different experiences. Forex trading is investment-oriented — digital, fast-moving, and profit-driven. It involves buying and selling currencies in pairs (like USD/IDR) with the goal of taking advantage of small price movements. Money changers, on the other hand, serve people who need actual, physical currency — for travel, business purchases, or personal remittances. In Indonesia, this distinction matters. The term Forex Indonesia increasingly refers to both the digital trading world and the everyday cash conversion economy, even though they operate in entirely separate lanes.
Forex Indonesia: How does forex trading work in the Indonesian context?
Forex trading in Indonesia has grown significantly, especially with the rise of mobile apps and international brokers that cater to local users. At its core, forex trading means speculating on the price movement of currency pairs. This happens through regulated platforms where traders can go long (buy) or short (sell) based on market trends, economic events, or geopolitical developments. Transactions are fully digital — no physical money is exchanged — and traders use tools like charts, signals, and indicators to guide their decisions.
Unlike changing money at a counter, trading forex is not about immediate use of currency. It’s about forecasting, timing, and risk. Leverage is often involved, meaning you can control a larger amount of money with a smaller deposit — but this also means losses can be magnified. The Indonesian government, through BAPPEBTI, strictly regulates this space. Only licensed brokers are permitted to operate, and users are encouraged to verify platforms before depositing funds. In this side of Forex Indonesia, the learning curve is steep, but the reach is global.
Forex Indonesia: How do money changers operate, and what purpose do they serve?

Source: Baliholidaysecrets
Money changers remain a familiar presence in malls, tourist hubs, and business centers across Indonesia. They provide a simple, immediate service — you walk in with rupiah and walk out with a different currency, like yen, euro, or USD. These services are especially useful for travelers, overseas students, or those sending money to family abroad. It’s a tangible, in-person process, usually accompanied by a printed receipt and a clear rate board posted on-site.
In Indonesia, all licensed money changers are monitored by Bank Indonesia, which ensures fair pricing and transparency. They follow compliance rules such as Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures, and they’re often easier to access for people who aren’t familiar with digital platforms. While this part of Forex Indonesia may feel more traditional, it continues to play an important role in real-world transactions — particularly in rural areas or for users who prefer dealing with physical cash.
Forex Indonesia: Are both services legal and regulated in Indonesia?

Source: Pasardana
Yes — but under different authorities. This is a crucial detail. Traditional money changers fall under the regulatory umbrella of Bank Indonesia, while forex trading activities are overseen by BAPPEBTI. The separation ensures that both sectors are supervised appropriately based on their risk levels and market roles.
Forex brokers must be officially registered and fulfill certain legal and financial obligations to offer services within Indonesia. Meanwhile, money changers must maintain clear records, report large transactions, and undergo regular audits. When engaging with either type of service, users should always check for licensing or registration status. This is particularly important in the digital space, where many unlicensed brokers from abroad target Indonesian clients under the radar. If you’re navigating Forex Indonesia, understanding these legal boundaries is essential for protecting your money.
Which option is better for the average Indonesian?

Source: Abu Sheikha
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer — it all depends on your purpose. If you’re heading overseas or need to receive physical foreign currency, a money changer is the practical choice. You get what you need on the spot, with no speculation or financial risk involved. The process is clear, familiar, and ideal for low-stress currency handling.
Forex trading, by contrast, is better suited for individuals looking to explore currency markets as an investment opportunity. It offers potential returns, but also carries significant risk. It’s best for those with the time to study market behavior, learn technical analysis, and monitor economic events. For many people new to finance, starting with a money changer and later exploring forex trading through small, supervised accounts is a safer path. In this way, the Forex Indonesia landscape supports both the casual user and the informed trader.
How do exchange rates compare?
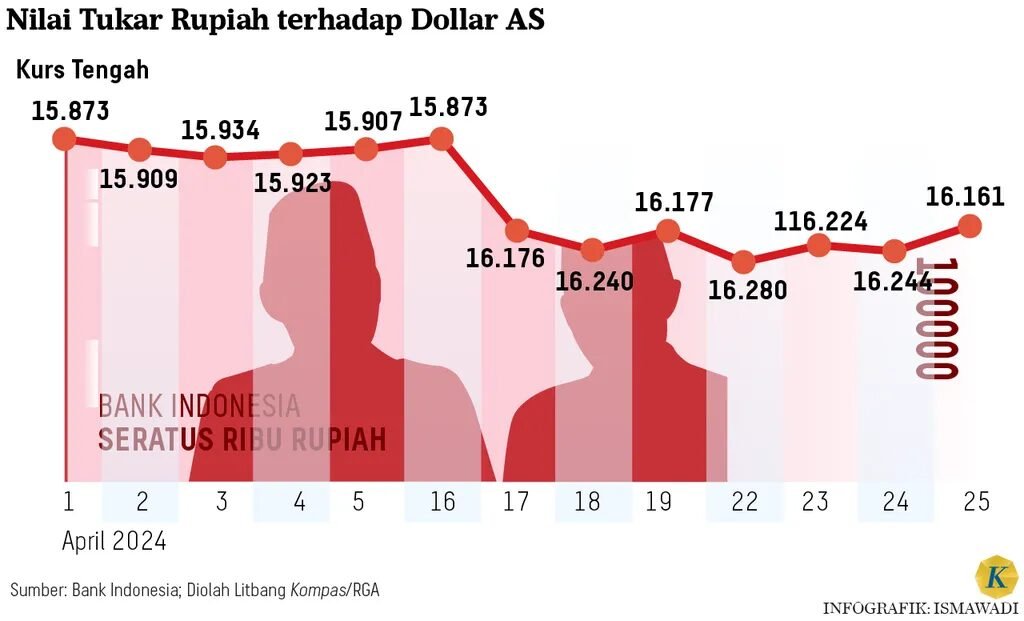
Source: Kompas
The way exchange rates are presented and applied is another key difference. Money changers display rates for buying and selling currencies, often including a service margin in the rate itself. This spread can vary depending on the outlet’s location, the currency’s popularity, or even the day’s demand. You might notice better rates in high-volume centers like Jakarta or Bali compared to smaller towns.
In contrast, forex trading platforms reflect near real-time interbank rates — the kind used by large financial institutions. These platforms make money through spreads or commissions, and while their rates may seem more accurate or favorable, they’re also tied to more volatile market conditions. If you’re looking for cost efficiency and speed for digital transactions, forex trading could offer better value. But for one-off or travel-based needs, a trusted money changer offers stability and predictability. Both have a place in the broader conversation around Forex Indonesia.
Who uses each type of service?

Source: IONgroup
The users of these services differ significantly. Money changers cater to a broad audience — tourists, expats, small business owners, and families. Their services are rooted in day-to-day practicalities. You exchange what you need and walk away with bills in hand. These customers usually care more about convenience than chasing small differences in exchange rates.
On the flip side, forex traders in Indonesia tend to be younger, digitally engaged, and financially curious. Many are attracted by the idea of trading as a side income, while others pursue it as a long-term skill. Trading forums, Telegram groups, and financial literacy campaigns are growing in popularity across the country. This new wave of users is helping to reshape the public perception of Forex Indonesia from something risky and unknown to something worth learning — with caution.
Conclusion
When people talk about Forex Indonesia, they’re often referring to a complex mix of old and new — digital platforms that offer global market access, and traditional money changers that serve everyday financial needs. Both systems deal in currencies, but they differ greatly in method, risk, and purpose. Whether you’re exchanging money for a holiday or diving into the global forex market, knowing the difference can save you time, money, and trouble. The financial landscape is evolving fast — but in Indonesia, both trading and physical exchange continue to play vital roles for very different types of users.




